Let’s be real, taxes aren’t exactly anyone’s favorite topic, but they keep the world running. The problem? Not everyone plays fair. According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), governments worldwide lose an estimated $600–700 billion every year due to tax evasion and avoidance (IMF, 2023 That’s money that could have gone into healthcare, education, or infrastructure.
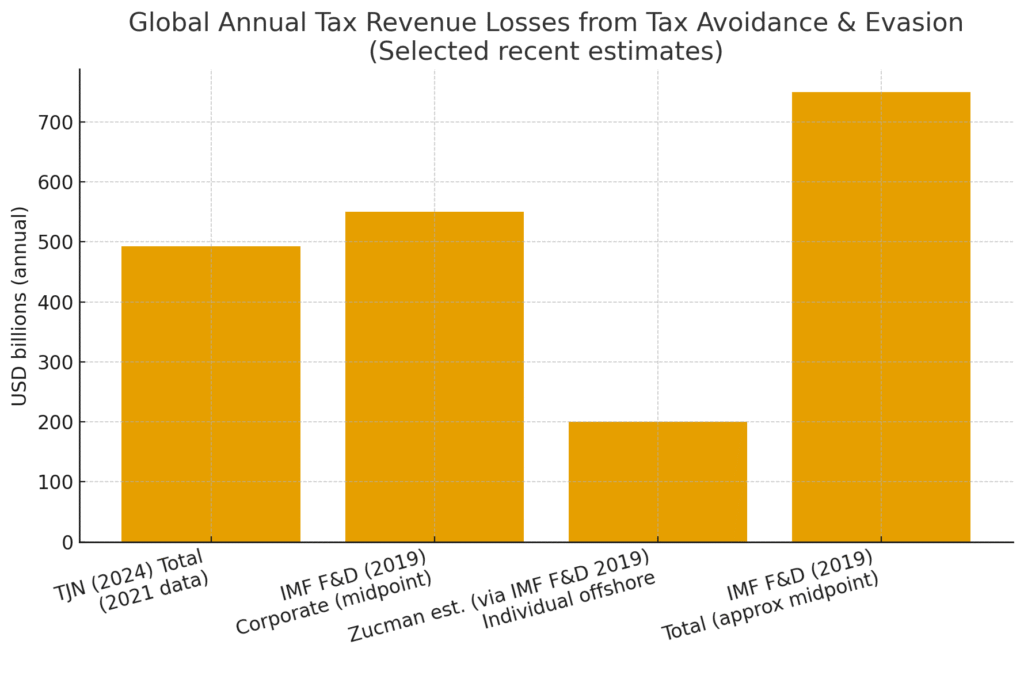
Because of these massive losses, governments across the globe invest billions into tax detection, the process of uncovering unreported income, fraudulent filings, or shady financial moves that reduce tax revenue. From advanced data analytics to artificial intelligence, the methods being used today are more sophisticated than ever before.
In this guide, we’ll break down what tax detection really means, why it matters, and how different countries approach it. We’ll also look at real-world case studies, the tools and technologies used, and even the challenges authorities face in catching fraudsters. My goal is simple: by the end, you’ll understand not just the concept, but also how modern tax systems are evolving to close the gaps.
What is Tax Detection?
Okay, let’s start simple. Imagine you and a group of friends are splitting a dinner bill. Everyone is supposed to chip in fairly, but one friend quietly “forgets” to add their share. If nobody notices, that friend walks away saving money while everyone else pays extra. Now scale that up to a national level, that’s basically what happens when people or businesses evade taxes. And just like you’d double-check the bill, governments use tax detection to spot those who aren’t paying their fair share.
At its core, tax detection is the process of identifying errors, omissions, or deliberate fraud in tax reporting. It’s not only about catching criminals, it also ensures honest taxpayers don’t end up carrying the burden of those who cheat the system.
Tax Detection vs. Tax Evasion
Here’s a quick distinction:
- Tax Evasion: The act of deliberately avoiding taxes (e.g., hiding income, using fake invoices, offshore accounts).
- Tax Detection: The set of methods and systems used by governments to uncover these tricks.
Think of evasion as the “crime” and detection as the “investigation.”
Key Differences Between Tax Evasion and Tax Detection
| Aspect | Tax Evasion 🕵️♂️ (the “crime”) | Tax Detection🔍 (the “investigation”) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Illegal practice of avoiding taxes by hiding income or falsifying records. | Process of identifying, investigating, and addressing tax evasion or errors. |
| Intent | Deliberate and deceptive. | Preventive and corrective. |
| Actors | Individuals or businesses trying to avoid taxes. | Governments, tax authorities (IRS, OECD, etc.). |
| Methods | Underreporting income, fake invoices, offshore accounts. | Audits, data analytics, AI, cross-border reporting. |
| Impact | Reduces government revenue, shifts burden to honest taxpayers. | Recovers revenue, ensures fairness, funds public services. |
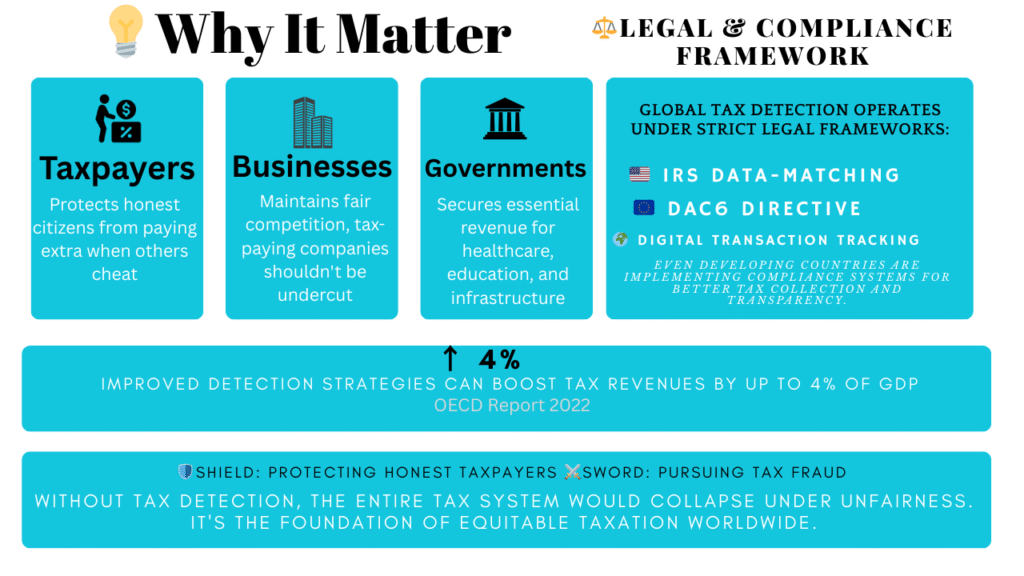
Why It Matters
Tax detection matters on multiple levels:
- For taxpayers: It protects honest citizens from paying extra when others cheat.
- For businesses: It maintains fair competition—companies that pay taxes shouldn’t be undercut by those that dodge them.
- For governments: It secures essential revenue for public services like healthcare, education, and infrastructure.
According to the OECD (2022), improved detection and compliance strategies can boost tax revenues by up to 4% of GDP in some countries (OECD Report
Legal & Compliance Framework
Globally, tax detection isn’t a free-for-all—governments operate under strict legal frameworks. In the U.S., the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) uses data-matching programs, audits, and reporting requirements. In the EU, directives like DAC6 require cross-border transparency. Even developing countries are rolling out compliance systems to track digital transactions.
In short, tax detection is both a shield (protecting honest taxpayers) and a sword (pursuing fraud). Without it, the whole tax system would collapse under unfairness.
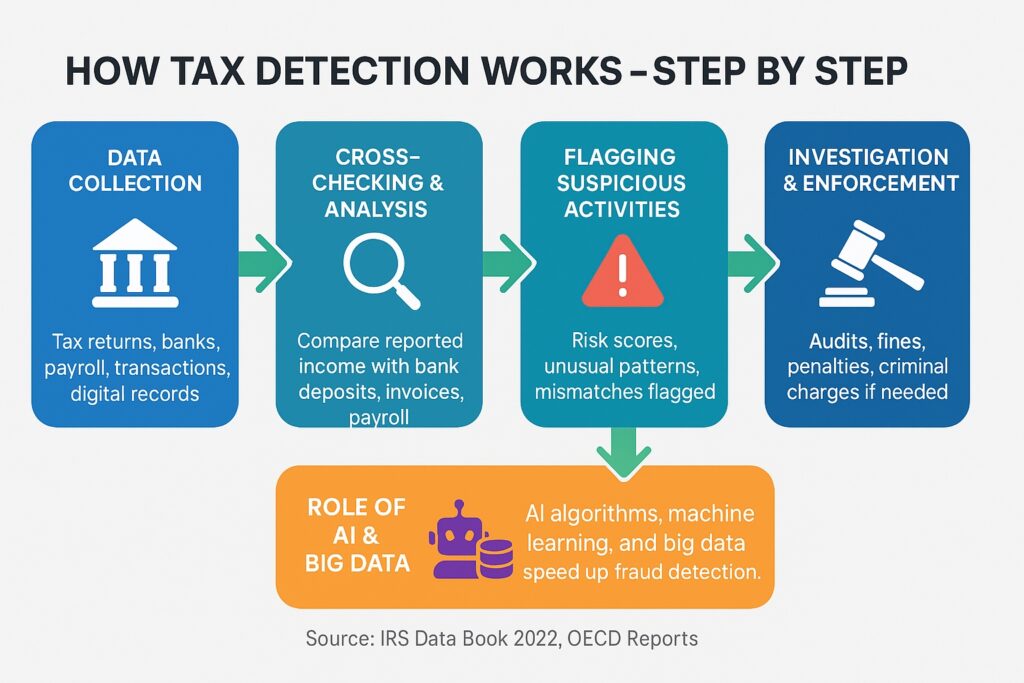
How Does Tax Detection Work?
Honestly, tax detection isn’t rocket science, it’s more like detective work with data. Let me walk you through the process step by step.
Step 1: Data Collection
Governments start by gathering tons of financial info, like:
- Tax returns (what you report)
- Bank and payroll records (what others report about you)
- Big transactions (real estate, credit cards, online sales)
💡 Basically, if money moves, there’s usually a digital trail.
Step 2: Cross-Checking & Analysis
Here’s where things get interesting:
- If you report $50k income, but banks show $100k deposits → 🚩 suspicious.
- If a business keeps “losing money” year after year, but payroll and suppliers don’t match → 🚩 suspicious.
Think of it like matching receipts after a night out, if numbers don’t add up, something’s fishy.
Step 3: Flagging Suspicious Activities
The system assigns a risk score. High-risk cases get flagged for audits.
Examples:
- Offshore transfers not declared
- Sudden spikes in income
- Repeated false expense claims
Step 4: Investigation & Enforcement
This is where humans step in:
- Audits for smaller mismatches
- Fines & penalties for bigger ones
- Criminal charges for outright fraud
In fact, the IRS recovered $68 billion in unpaid taxes in 2022 alone (IRS Data Book
Where AI & Big Data Come In
Here’s the cool part: computers now do most of the heavy lifting.
- AI spots unusual patterns at lightning speed.
- Machine learning keeps improving accuracy.
- Big data compares millions of records in seconds.
The IRS even uses a system called DIF (Discriminant Inventory Function System), which gives every tax return a “score.” The higher the score, the more likely you’ll get audited.
A Quick Example
Let me tell you about one case: A small business claimed just $200k in revenue, but banks showed $500k in deposits. Add in mismatched payroll filings, and boom, IRS flagged it. After an audit, they were fined for underreporting income.
Moral of the story? Tax detection is basically Sherlock Holmes with spreadsheets (and now AI).
Here’s a simple flowchart that shows how tax detection actually works, step by step:
Types of Tax Detection Methods
When it comes to catching tax evasion, governments don’t rely on a single trick. They use a mix of old-school manual audits and modern automated systems powered by AI and data analytics. Let’s break these down.
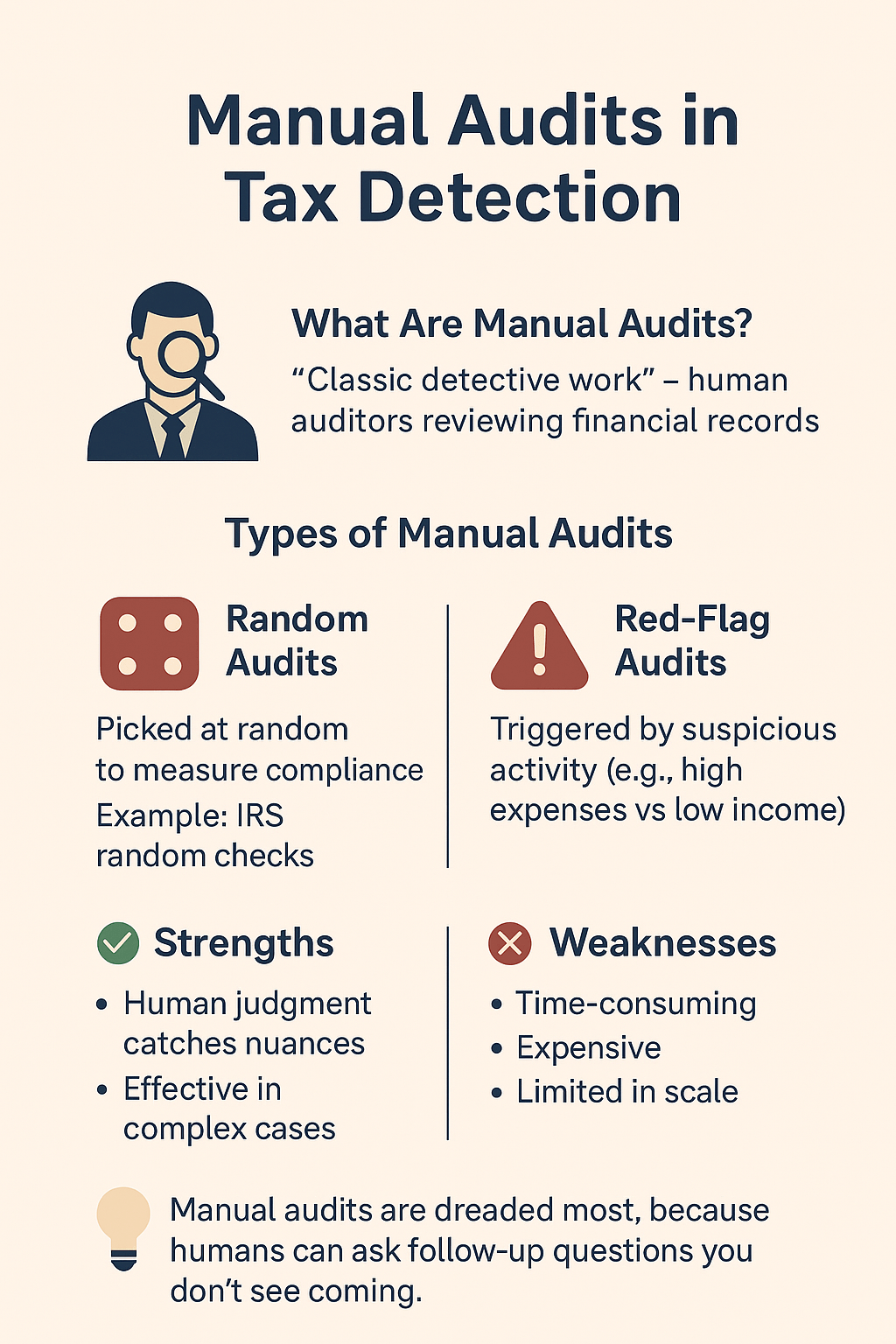
Manual Audits (Traditional Inspections)
Think of manual audits as the “classic detective work” of tax detection. Here, human auditors review a taxpayer’s financial records line by line, checking receipts, invoices, payroll documents, and bank statements.
Two types of manual audits exist:
- Random Audits: These are like lucky (or unlucky) draws. A small percentage of tax returns are picked at random just to keep everyone on their toes. The IRS, for instance, conducts random audits each year to measure compliance levels across the population.
- Red-Flag Audits: These are triggered when something looks suspicious. For example, if your expenses seem way too high compared to your income, or your business shows losses for five years straight, you might land in this category.
Strengths:
- Human judgment can catch nuances that algorithms might miss.
- Useful for complex cases (like multinational corporations using loopholes).
Weaknesses:
- Time-consuming and costly.
- Limited in scale, you can’t manually check millions of taxpayers.
In my experience, people dread manual audits the most, because unlike algorithms, humans can ask follow-up questions you didn’t see coming.
Automated Detection Systems
Now let’s talk about the modern era, where computers and AI do most of the heavy lifting. Automated systems scan millions of tax returns in seconds, flagging anything unusual.
How they work:
- Algorithms & Predictive Analytics: These compare your tax return with benchmarks. If your expenses are 200% higher than the industry average, that’s suspicious.
- Pattern Recognition: The system looks for trends, like consistent underreporting of income, fake invoices, or repeated small transactions that add up.
- AI-Driven Anomaly Detection: Artificial Intelligence doesn’t just look for exact matches; it spots behavior that simply doesn’t “fit.” For example, if a small coffee shop suddenly reports foreign income from three different countries, the system knows something’s off.
Real-world example:
The IRS uses a program called DIF (Discriminant Inventory Function System), which assigns a “score” to every tax return. The higher the score, the more likely it’s flagged for audit. Similar AI-driven systems are also used in the UK (HMRC’s Connect system) and Australia (ATO’s risk engines).
Strengths:
- Scalable: can process millions of records quickly.
- Objective: algorithms don’t play favorites.
- Cost: effective compared to manual labor.
Weaknesses:
- False positives (sometimes honest taxpayers get flagged).
- Relies on quality of input data, garbage in, garbage out.
Let me tell you, AI may not replace human auditors completely, but it makes their job 10x faster and sharper. Think of it as a metal detector at the airport, it won’t arrest anyone, but it will point security to the right bag.
Bottom Line:
Manual audits are like Sherlock Holmes, detailed, slow, but precise. Automated systems are like AI-powered surveillance cameras, scanning everyone all the time. Together, they form a powerful combo to keep tax evasion in check.
Key Differences Between Manual Audits and Automated Tax Detection Systems
| Feature / Aspect | Manual Audits 📝 (Traditional) | Automated Systems 🤖 (Modern) |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Human auditors review tax returns, receipts, and records. | Algorithms & AI scan millions of records automatically. |
| Audit Type | Random or red-flag based. | Risk scoring, predictive analytics, anomaly detection. |
| Strengths | Human judgment, flexible, catches complex cases. | Fast, scalable, objective, cost-efficient. |
| Weaknesses | Time-consuming, expensive, limited coverage. | False positives, data-quality dependent, less nuance. |
| Best For | Complex frauds, multinational cases, detailed reviews. | Large-scale screening, early fraud detection, high-risk flagging. |
| Example | IRS agents conducting field audits. | IRS DIF system, UK HMRC “Connect,” ATO risk engines. |
Common Tax Detection Triggers
Ever wondered what makes the IRS (or any tax authority) raise an eyebrow? In my experience, most people don’t realize that tax detection triggers are actually patterns and inconsistencies that stand out in financial data. It’s not always about being rich or filing late, it’s about mismatches. Let’s break it down point by point.
1. Inconsistent Income vs Lifestyle
Imagine someone reporting a modest $40,000 income, but driving a brand-new luxury car, taking international vacations, and posting about it on Instagram. Tax agencies use lifestyle audits to compare reported income with visible wealth. If your lifestyle doesn’t match your declared earnings, that’s a red flag for tax detection.
2. Unusual Deduction Patterns
Claiming deductions is normal, but unusual patterns can trigger closer looks.
For example:
- Reporting very high charitable donations compared to income.
- Writing off “business expenses” that clearly look personal (like vacations labeled as “client meetings”).
- Excessive home office deductions.
These don’t always mean fraud, but they can flag your return for deeper review.
3. Cash-Heavy Businesses
If you run a business where most transactions are in cash, like restaurants, salons, or convenience stores, tax agencies pay extra attention. Why? Because cash transactions are harder to track, making underreporting income tempting. Modern tax detection systems now use data analytics to spot patterns where cash-heavy businesses declare suspiciously low profits.
4. International Transactions
Global money transfers are another common trigger. Sending or receiving large sums overseas—especially to countries with low transparency, can spark interest. Tax authorities often collaborate internationally (through frameworks like FATCA and OECD agreements) to track hidden assets abroad.
5. Industry-Specific Red Flags
Every industry has its quirks. For example:
- Construction → “off-the-books” workers, unreported subcontractor payments.
- Freelancers & gig workers → underreporting income from multiple platforms.
- Medical practices → cash co-payments not fully reported.
Tax authorities know these patterns and design detection models specific to each industry.
Quick Reference Table: Common Tax Detection Triggers
| Trigger | Why It Raises Flags |
|---|---|
| Inconsistent income vs lifestyle | Spending > Reported earnings (luxury goods, travel, assets) |
| Unusual deduction patterns | Deductions disproportionate to income |
| Cash-heavy businesses | Hard-to-track transactions, potential underreporting |
| International transactions | Possible offshore tax evasion, hidden accounts |
| Industry-specific red flags | Known high-risk behaviors (construction, medical, freelance) |
Tax Detection in the USA
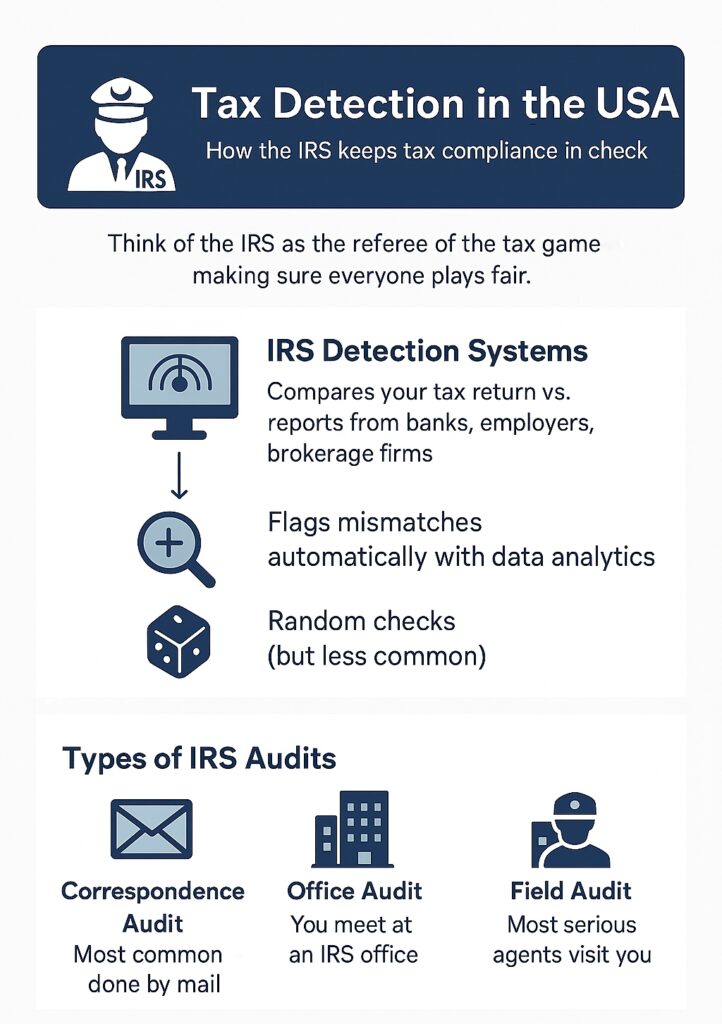
When it comes to tax detection in the USA, the IRS (Internal Revenue Service) is the ultimate watchdog. Think of it like this: if filing your taxes is a game, the IRS is the referee making sure everyone plays fair. And believe me, their detection tools are far more advanced than most people realize.
IRS Audit Systems & Methods
The IRS doesn’t just pick tax returns at random (though that can happen). Most of the time, it uses sophisticated tax detection systems to scan millions of returns. They compare what you file with what your bank, employer, or brokerage firms report. If something doesn’t line up, boom, your return could get flagged.
the agency runs different types of audits:
- Correspondence audits (handled by mail, the most common).
- Office audits (where you visit the IRS).
- Field audits (the most serious, where IRS agents come to you).
👉 In my experience, most taxpayers never face the scary “field audit.” Instead, they’re asked to provide documents through the mail. But still, the process can be stressful if your numbers don’t add up.
Top IRS Triggers to Watch Out For (2024–2025)
So, what really catches the IRS’s eye? Here are the most common IRS audit triggers:
- Self-Employed Income (Schedule C Filers) – Freelancers, gig workers, and small business owners get extra scrutiny since they can easily overstate expenses.
- High Deductions Compared to Income – Claiming unusually high medical, travel, or business deductions can trigger closer inspection.
- Cryptocurrency Transactions – Since 2023, the IRS has doubled down on crypto tax audits. According to the IRS digital assets.
Failure to report Bitcoin, Ethereum, or NFT sales is a top enforcement priority.
- Cash-Intensive Businesses – Restaurants, salons, laundromats, and convenience stores often attract audits because cash is harder to track.
- International Transfers & Offshore Accounts – Thanks to FATCA rules
👉 Bottom line? If you’re self-employed, dealing with crypto, or running a cash-heavy business, you’re automatically on the IRS’s “watch list.” The key is not to panic, but to keep clean records and file honestly. In today’s world, tax detection in the USA is sharper than ever.
IRS Audit Types & Triggers: Quick Comparison
| Audit Type / Trigger | How It Works | Risk Level | Who Gets Targeted Most |
|---|---|---|---|
| Random Audit | IRS selects some returns randomly for review. | Low | Any taxpayer (rare, less than 1% chance). |
| Red-Flag Audit | Algorithms flag unusual patterns (e.g., income vs deductions mismatch). | High | Freelancers, small biz owners, high deduction filers. |
| Self-Employed Income (Schedule C) | IRS checks for overstated expenses, underreported income. | High | Gig workers, freelancers, contractors. |
| Crypto Transactions | IRS monitors digital assets (Bitcoin, Ethereum, NFTs). | Rising | Crypto investors, traders, NFT sellers. |
| Cash-Heavy Businesses | Hard-to-track cash flow often triggers audits. | Medium–High | Restaurants, salons, laundromats, convenience stores. |
| International Transfers | Large or undeclared foreign accounts flagged under FATCA rules. | Very High | Expats, offshore account holders. |
Tax Detection in Other Countries
When it comes to tax detection, every country has its own playbook. But the end goal is the same everywhere, make sure taxpayers stay compliant. Let’s take a world tour and see how different governments are cracking down on tax evasion.
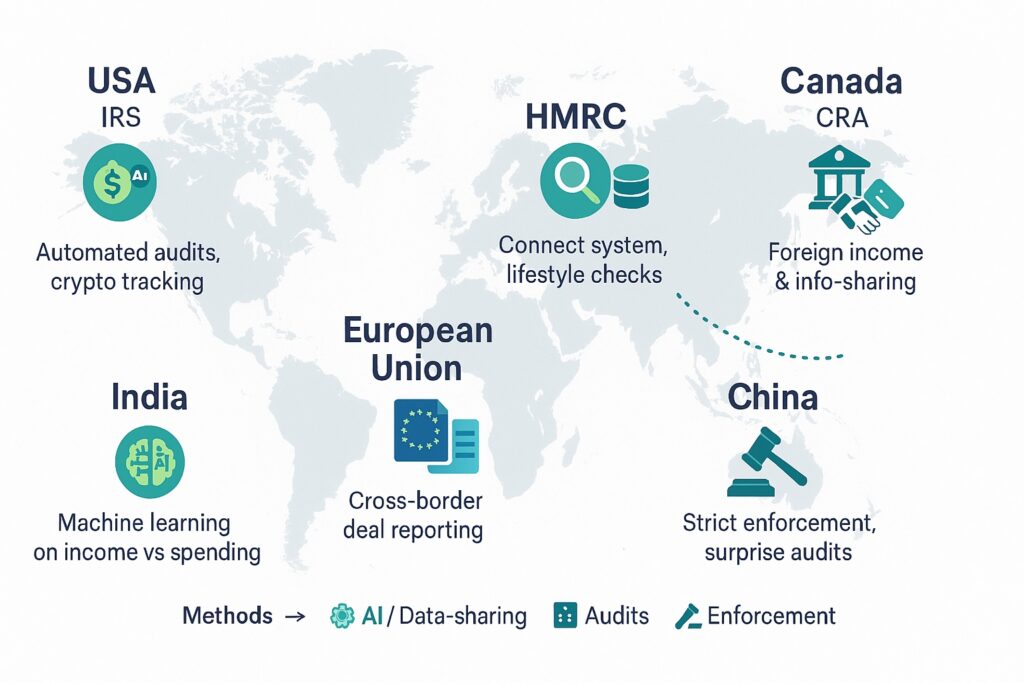
United Kingdom (HMRC)
The UK’s tax authority, HMRC, uses something called the Connect system, an AI-powered database that pulls information from banks, property records, and even social media. According to HMRC’s official report, the UK faced a £36 billion “tax gap” in 2022–23 (HMRC, 2023) This system once flagged a person driving a luxury car while reporting minimum wage income, classic mismatch detection.
Canada (CRA)
Canada’s Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) has one of the toughest stances on offshore tax evasion. They actively exchange information with 100+ countries through the OECD’s Common Reporting Standard. In 2021, CRA investigations helped identify CAD $1.2 billion in unpaid taxes ourcommons.ca Offshore secrecy? Pretty much dead in Canada.
European Union (DAC6)
The EU rolled out DAC6 rules, requiring companies and tax advisors to report cross-border arrangements. By 2023, over 100,000 arrangements had been flagged across Europe (European Commission, 2023) This isn’t just about individuals, it’s about stopping complex corporate loopholes.
India
India has gone all-in on AI-powered tax detection. Their systems cross-check lifestyle expenses with declared income. In 2021 alone, authorities shut down 20,000 shell companies linked to tax evasion and money laundering (Indian Ministry of Finance, 2021) If your spending habits don’t match your reported salary, you’re on their radar.
China
China still relies on a mix of digital surveillance and surprise audits. A major crackdown in 2022 recovered billions in lost VAT revenue, particularly in manufacturing and exports (China State Taxation Administration, 2022) When they say “compliance,” they don’t mess around.
Global Tax Detection Methods: At a Glance
| Country/Region | Detection Method | Unique Feature / Example |
|---|---|---|
| United Kingdom (HMRC) | AI-powered Connect system | Cross-checks bank, property & even social media; flagged luxury car owner with low declared income |
| Canada (CRA) | International data-sharing (OECD CRS) | Identified CAD $1.2B unpaid taxes in 2021 |
| European Union (DAC6) | Mandatory disclosure of cross-border deals | Over 100,000 tax arrangements flagged in 2023 |
| India | AI & lifestyle-income mismatch detection | Shut down 20,000 shell companies in 2021 |
| China | Digital surveillance + surprise audits | Billions recovered from VAT fraud (2022 crackdown) |
Real-Life Case Studies in Tax Detection
You know, reading about tax systems in theory is okay, but real-life stories? That’s where things get interesting. Let me share two memorable cases, one involving corporate fraud and the other an individual case, with sources you can check yourself.
1. Corporate Fraud Uncovered: The Enron Scandal
Remember Enron? Once a Wall Street darling, it crashed under the weight of its own lies. Executives used secret partnerships, misreported debts, and cooking-the-books tactics to inflate earnings. The fallout? Bankruptcy, massive investor losses, and laws like the Sarbanes-Oxley Act aimed at preventing future scandals. The FBI even set up a multi-agency task force, seizing documents from Enron’s HQ (over 3,000 boxes!) to build their case. Wikipedia+ Federal Bureau of Investigation
Lesson: Even mega-corporations can’t hide when analysts, auditors, and investigators dig deep into financials, and enforcement systems are built to respond.
2. Individual Tax Evasion: Wesley Snipes
Hollywood’s Blade star, Wesley Snipes, earned millions but skipped filing his tax returns for years. The IRS flagged it via data cross-checks. After a trial, though acquitted on felony counts, Snipes was convicted of misdemeanor failure to file and sentenced to three years, serving 28 months. The government even disputed his claim of being a “non-resident alien,” which he made while resisting IRS subpoenas. Wikipedia+ Department of Justice
Lesson: No matter how famous you are, tax systems catch up. The tools they use—cross-checks, court records, don’t discriminate.

How to Stay Compliant & Avoid Red Flags
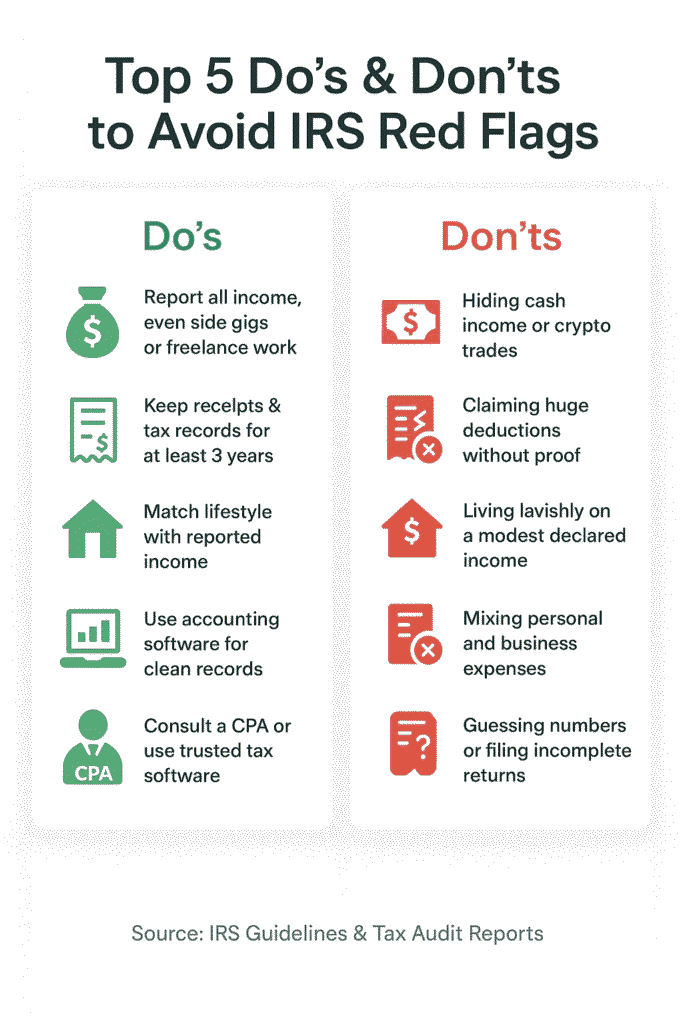
So here’s the million-dollar question: “How do I avoid getting into trouble with tax authorities?” Trust me, you’re not the only one who worries about that dreaded audit letter from the IRS. The good news? Staying compliant isn’t rocket science. It mostly comes down to being consistent, transparent, and smart about your money trail.
✅ For Individuals: Everyday Habits That Save Stress
- Report all income (yes, all of it): Even side hustles, freelance gigs, or Venmo payments for services can be taxable.
- Don’t overdo deductions: Claim what you’re entitled to, but if your write-offs look way out of proportion to your income, that’s a red flag.
- Keep records handy: Hold on to receipts, 1099s, W-2s, and bank statements for at least three years.
- Match lifestyle with income: If you report $40,000 but buy a Tesla and a beach house, the math won’t add up for the IRS.
🏢 For Businesses: Play It Clean
- Transparent bookkeeping. Use proper accounting software instead of spreadsheets. It makes reporting easier and keeps you safe if questions arise.
- Payroll compliance matters. Report employee salaries and withholdings correctly. IRS payroll audits are among the most common triggers.
- Cash-heavy operations, beware. Restaurants, salons, and retail shops attract extra scrutiny. Document everything carefully.
- International dealings? Report them. If you’re wiring money abroad or receiving foreign funds, disclose them properly. Thanks to agreements like FATCA and the OECD’s CRS, hidden accounts are much harder to keep secret.
💻 Special Note: Crypto & the New Economy
Crypto traders, listen up. Platforms like Coinbase and Binance already report user activity to the IRS. And starting in 2025, exchanges must issue Form 1099-DA, which means your Bitcoin, Ethereum, or NFT trades will be automatically flagged if left off your return. (IRS Digital Assets info)
Same goes for gig apps (Uber, DoorDash, Upwork). They issue 1099 forms, and those get cross-checked against your tax return automatically.
👨💼 When in Doubt, Get Professional Help
Honestly, the cost of hiring a tax professional or using reliable tax software is nothing compared to the stress of an audit. Even a single consultation with a CPA can save you from expensive mistakes. IRS Directory of Tax Return Preparers is a good place to start if you need help.
Useful LINKS
- 2025 Tax Brackets Explained Simply: Save More with Smart Tax Hacks
- Tax Credits 101: Your Complete Guide to Saving Money on Taxes in 2025
- how To Create A Personal Or Family Budget 2025
FAQs About Tax Deductions & Income
What is a tax deduction?
Quick Answer: A tax deduction reduces your taxable income, which means you pay less in taxes.
Detailed Answer:
Think of a tax deduction as the government’s way of saying, “Okay, you spent money on something important, so we’ll cut you some slack on your taxes.” Tax detection itself is the process where tax authorities check incomes, business records, and transactions to ensure people and companies are paying fairly. They use audits, financial reviews, and even data algorithms to uncover hidden income or fake expenses.
As tax expert Jeff A. Schnepper explains in his book How to Pay Zero Taxes: “A deduction is not a dollar-for-dollar refund, but it lowers the amount of income the government can tax.”
What is a wage tax deduction?
Quick Answer: It’s the income tax your employer automatically withholds from your paycheck and sends to the government.
Detailed Answer:
Whenever you get paid, a portion of your salary doesn’t go into your pocket, it goes straight to the IRS. This is called wage tax deduction. Your employer calculates the amount based on tax brackets, allowances, and legal requirements, then forwards it to the government. The money left is your take-home pay.
This system makes paying taxes easier for employees since you don’t have to worry about setting money aside yourself.
How do you calculate taxable income?
Quick Answer: Start with your gross income, subtract tax-exempt amounts and deductions, then add taxable gains.
Detailed Answer:
Calculating taxable income is like solving a puzzle:
1. Begin with gross income (everything you earn).
2. Subtract any exempt income (like certain allowances).
3. Deduct all allowed tax deductions (business expenses, investments, donations).
4. Add any capital gains if you sold property or assets.
The result is your taxable income, the figure the IRS uses to calculate how much you owe.
Can I claim myself as a deduction?
Quick Answer: Not anymore in the U.S. — personal exemptions were removed, but self-employed individuals can claim business-related expenses.
Detailed Answer:
Previously, Americans could claim a “personal exemption” for themselves, but that rule was eliminated with tax law changes. Now, you can’t deduct yourself directly. However, if you’re self-employed, you may deduct certain expenses tied to your work, like travel costs, office supplies, or software.
Remember: you don’t get a tax break just for existing, only for legitimate, documented expenses.
What is the deduction-eligible income?
Quick Answer: Deduction-Eligible Income (DEI) is the portion of a company’s income that qualifies for special tax deductions.
Detailed Answer:
Here’s how it works: corporations calculate their gross income, subtract specific excluded categories (like certain dividends), and then deduct qualified expenses. What remains is DEI, which is particularly relevant for calculating special deductions like Foreign-Derived Intangible Income (FDII).
This concept matters more for corporations than individuals, but it’s a key part of international tax planning.
How does income tax work in the Netherlands for foreigners?
Quick Answer: Foreigners working in the Netherlands pay tax under the Dutch “box system,” with different rates for salary, investments, and substantial shareholdings.
Detailed Answer:
If you’re working or earning in the Netherlands, you may be treated as a tax resident. The system breaks down into three boxes:
Box 1 (Salary & Home Ownership): 2025 rates are 35.82% up to €38,441, 37.48% up to €76,817, and 49.5% above that.
Box 2 (Substantial Interest): 24.5% or 31% if you hold 5%+ shares in a company.
Box 3 (Savings & Investments): Flat 36%, with a €57,684 tax-free allowance per person.
This system ensures taxes are applied fairly depending on the type of income. For many expats, the 30% ruling can also apply, which gives a tax break on a portion of your salary if you meet the conditions.
Pingback: Tax Crimes vs Tax Evasion: Stay Safe from IRS Penalties 2025